Impact of 3D Cloud Structures on the Atmospheric Trace Gas Products from UV-VIS Sounders
17.11.2021
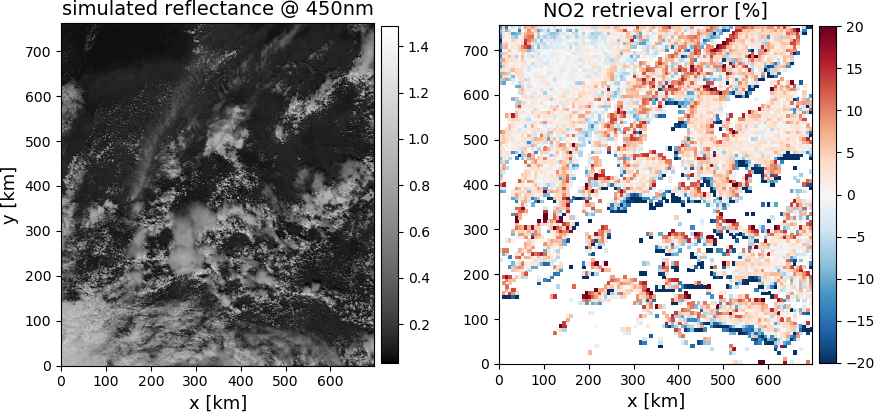
Retrievals of trace gas concentrations from satellite observations are mostly performed for clear regions or regions with low cloud coverage. However, even fully clear pixels can be affected by clouds in the vicinity, either by shadowing or by scattering of radiation from clouds in the clear region.
Within the ESA project 3DCATS (Impact of 3D Cloud Structures on the Atmospheric Trace Gas Products from UV-VIS Sounders) we have quantified cloud related retrieval bias in NO2 tropospheric vertical column density (TVCD).
We have used our 3D radiative transfer model MYSTIC to generate synthetic including including as input 3D cloud structures based on high-resolution large eddy simulations (ICON model). Retrieval algorithms were applied on
the synthetic data and comparison to the known input trace gas concentrations yields the retrieval error due to cloud scattering. In order to quantify the NO2 TVCD bias based on real observations we used the NO2 data product from the TROPOspheric Monitoring Instrument (TROPOMI) and in addition the cloud products from the Visible Infrared
Imaging Radiometer Suite (VIIRS). We found in both, synthetic and observational data, that for solar zenith angles smaller than about 40° the NO2 TVCD bias is typically below 10%, whereas for lager zenith angles the bias increases to values larger than 20%. We therefore used the synthetic data to investigate the relations between various cloud parameters and the NO2 TVCD bias. Based on this analysis we developed first concepts to correct for 3D cloud
scattering in trace gas retrieval algorithms.
- Emde, C., Yu, H., Kylling, A., van Roozendael, M., Stebel, K., Veihelmann, B., and Mayer, B.: Impact of 3D Cloud Structures on the Atmospheric Trace Gas Products from UV-VIS Sounders – Part I: Synthetic dataset for validation of trace gas retrieval algorithms, Atmos. Meas. Tech. Discuss. [preprint], https://doi.org/10.5194/amt-2021-336, in review, 2021.
- Yu, H., Emde, C., Kylling, A., Veihelmann, B., Mayer, B., Stebel, K., and Van Roozendael, M.: Impact of 3D Cloud Structures on the Atmospheric Trace Gas Products from UV-VIS Sounders - Part II: impact on NO2 retrieval and mitigation strategies, submitted to Atmos. Meas. Tech. Discuss. 2021
- Kylling, A., Emde, C., Yu, H., van Roozendael, M., Stebel, K., Veihelmann, B., and Mayer, B.: Impact of 3D Cloud Structures on the Atmospheric Trace Gas Products from UV-VIS Sounders – Part III: bias estimate using synthetic and observational data, Atmos. Meas. Tech. Discuss. [preprint], https://doi.org/10.5194/amt-2021-331, in review, 2021.

